Create an Object of Class 'mefa'
mefa.RdAn object of class 'mefa' is a compendium of a crosstabulated taxa-by-samples (count) data, and optionally (count) data for segments, and linked tables for samples and taxa. The 'mefa' term stand for an acronym of 'metafaunistics', indicating that data processing is a critical and often time consuming step before data analysis. The 'mefa' package aims to help in this respect.
Usage
mefa(xtab, samp = NULL, taxa = NULL, id.samp = NULL, id.taxa = NULL,
segment = TRUE, nested = FALSE, drop.zero = FALSE, drop.index = FALSE,
xtab.fixed = TRUE)
# S3 method for class 'mefa'
is(x)
# S3 method for class 'mefa'
print(x, nlist = 10, ...)
# S3 method for class 'mefa'
summary(object, nlist = 10, ...)
# S3 method for class 'summary.mefa'
print(x, nlist, ...)
# S3 method for class 'mefa'
dim(x)
# S3 method for class 'mefa'
dimnames(x)Arguments
- xtab
data. Can be an object of class 'stcs', or a matrix or data frame. Can be count (integer) or non-integer.
- samp
a data frame containing rows for samples, or
NULL. See argumentxtab.fixedand details for sample matching options.- taxa
a data frame containing rows for taxa, or
NULL. See argumentxtab.fixedand details for taxa matching options.- id.samp
NULLif sample names for matching are the rownames ofsamp, otherwise, the index refers to the column ofsampwhere the names are located.- id.taxa
NULLif taxa names for matching are the rownames oftaxa, otherwise, the index refers to the column oftaxawhere the names are located.- segment
logical, whether information in the segments column of the 'stcs' object should be used (
TRUE, default). It has no effect whenxtabis matrix or data frame.- nested
logical, whether segments should be nested within each other from the first to the last (
TRUE) or not (FALSE, default).- drop.zero
logical, if
TRUEempty samples are removed from the result (can be useful before multivariate analyses). Otherwise, empty rows are left intact (FALSE, default).- drop.index
logical, whether columns of the samples and taxa tables containing the names used for matching should be removed (
TRUE) to reduce redundancy or not (FALSE, default). This argument has effect only ifid.sampandid.taxaare notNULL.- xtab.fixed
logical, if
TRUE(default) thesampandtaxatables are subsetted and ordered according to the names ofxtab. IfFALSE,xtabis also subsetted according to the intersect of the names. Row and column ordering is determined byxtabin either cases.- x, object
an object of class 'mefa'.
- nlist
number of elements in the list of segment names to print. List of segment names is truncated at 10 by default.
- ...
other arguments passed to functions.
Details
Main goals of the mefa function are to (1) convert a long formatted object of 'stcs' into a crosstabulated and optionally segmented 'mefa' object and (2) link this crosstabulation with tables of samples and taxa. The segments can be nested within each other. This feature can be useful, if segments represent e.g. subsequent sampling periods (years) and the the aim is to detect effects of data accumulation over time.
A mefa object can be viewed as a project oriented compendium of the data. It contains 3 dimensional (samples, taxa, segments) representation of the count data and data tables for samples and taxa. Segments contain information on some particular internal division of the data (sub populations, method specific partitions, repeated measures), but it has technical significance. Thus data tables for segments are not supported.
Input values may contain non-integer values as well.
If the input xtab is a matrix, dimnames are necessary if either samp or taxa tables are provided. In other cases, dimnames are not necessary. In this way, simple statistics can be returned for the matrix.
The print method returns basic information, instead of a long structural representation.
The summary contains statistics calculated from the 'mefa' object (species richness, number of individuals, occupancy, abundance, total sum, matrix fill, etc., see 'Value' section). The list can be recalled by e.g. unclass(summary(x)), elements of the list e.g. summary(x)$s.rich.
Methods for extracting, subsetting, plotting and reporting 'mefa' objects are discussed elsewhere (see links in 'See also' section). On how the 'mefa' objects can be used in further analyses, see 'Examples' and the vignette (vignette("mefa")).
When the as.mefa function is used with a 'mefa' object as argument, samples and taxa tables are used when samp and taxa arguments are missing. If the aim is to redefine these tables, those also can be given.
Value
The mefa function returns an object of class 'mefa'. It is a list with 5 elements:
- call
the function call.
- xtab
crosstabulated count data, rows are samples, columns are taxa.
- segm
list of matrices if segments are used, otherwise
NULL.- samp
a data frame for sample related data (rows correspond to samples) if provided, otherwise
NULL.- taxa
a data frame for taxa related data (rows correspond to taxa) if provided, otherwise
NULL.
The summary.mefa function returns a list invisibly, with elements:
s.rich: vector with species richness values for the samples,
s.abu: vector with number of individuals values for the samples,
t.occ: number of sites occupied by each species,
t.abu: abundances of each species,
ntot: total number of individuals,
mfill: matrix fill,
nsamp: number of samples,
ntaxa: number of taxa,
nsegm: number of segments,
segment: vector of segment names,
call: the function call from the 'mefa' object,
nested, drop.zero, xtab.fixed: attributes of the 'mefa' object.
The method dim returns a vector of length 3 with values for number of samples, number of taxa and number of segments in the 'mefa' object. The third value is 1 in cases, when s$segm is NULL (because it is 1 undefined segment essentially identical to the matrix x$xtab, thus no need for a replicate).
The dimnames method returns a list of three character vectors for names of samples, taxa and segments. These can be NULL as well.
References
S\'olymos P. (2008) mefa: an R package for handling and reporting count data. Community Ecology 9, 125–127.
S\'olymos P. (2009) Processing ecological data in R with the mefa package. Journal of Statistical Software 29(8), 1–28. doi:10.18637/jss.v029.i08
Author
P\'eter S\'olymos, solymos@ualberta.ca
Note
The mefa function alone can be used instead of the combination of object classes xcount and xorder used in older (< 2.0) versions of the mefa package. Further it is also extended by previously undocumented features.
See also
Further methods are discussed on separate help pages: see [.mefa and aggregate.mefa for extracting and aggregating the data, melt.mefa for redefining segments or melting data into long format, report.mefa for generating report into file, and plot.mefa boxplot.mefa and image.mefa for graphical display.
See as.mefa for coercion methods.
Examples
data(dol.count, dol.samp, dol.taxa)
## Input is stcs
x1 <- mefa(stcs(dol.count))
x1
#>
#> An object of class 'mefa' containing
#>
#> $ xtab: 731 individuals of 28 taxa in 24 samples,
#> $ segm: 2 (non-nested) segments:
#> fresh, broken,
#> $ samp: table for samples not provided,
#> $ taxa: table for taxa not provided.
#>
## Input is matrix
x2 <- mefa(x1$xtab)
x2
#>
#> An object of class 'mefa' containing
#>
#> $ xtab: 731 individuals of 28 taxa in 24 samples,
#> $ segm: 1 (all inclusive) segment,
#> $ samp: table for samples not provided,
#> $ taxa: table for taxa not provided.
#>
## Attach data frame for samples
x3 <- mefa(stcs(dol.count), dol.samp)
x3
#>
#> An object of class 'mefa' containing
#>
#> $ xtab: 731 individuals of 28 taxa in 24 samples,
#> $ segm: 2 (non-nested) segments:
#> fresh, broken,
#> $ samp: table for samples provided (2 variables),
#> $ taxa: table for taxa not provided.
#>
## Attach data frame for samples and taxa
x4 <- mefa(stcs(dol.count), dol.samp, dol.taxa)
x4
#>
#> An object of class 'mefa' containing
#>
#> $ xtab: 731 individuals of 28 taxa in 24 samples,
#> $ segm: 2 (non-nested) segments:
#> fresh, broken,
#> $ samp: table for samples provided (2 variables),
#> $ taxa: table for taxa provided (4 variables).
#>
## Methods
## (chapter 'See also' provides
## links for further methods)
summary(x4)
#>
#> Call:
#> mefa(xtab = stcs(dol.count), samp = dol.samp, taxa = dol.taxa)
#>
#> Summary
#> Total sum 731
#> Matrix fill (%) 26
#> Number of samples 24
#> Number of taxa 28
#> Number of segments 2
#>
#> Segments (non-nested):
#> fresh, broken
#>
#> s.rich s.abu t.occ t.abu
#> Min. 0.000000 0.00000 1.000000 1.00000
#> 1st Qu. 5.000000 9.75000 2.000000 4.00000
#> Median 7.000000 20.50000 4.500000 10.50000
#> Mean 7.333333 30.45833 6.285714 26.10714
#> 3rd Qu. 10.000000 44.75000 10.000000 27.75000
#> Max. 16.000000 97.00000 23.000000 245.00000
#>
## Descriptives inside the summary
unclass(summary(x4))
#> $s.rich
#> DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DT1 DT2 DT3 LQ1 LQ2 LQ3 LT1 LT2 LT3 RQ1 RQ2 RQ3 RT1 RT2 RT3 WQ1 WQ2
#> 5 7 4 7 10 5 5 5 7 0 2 5 10 16 13 11 15 10 9 10
#> WQ3 WT1 WT2 WT3
#> 8 5 4 3
#>
#> $s.abu
#> DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DT1 DT2 DT3 LQ1 LQ2 LQ3 LT1 LT2 LT3 RQ1 RQ2 RQ3 RT1 RT2 RT3 WQ1 WQ2
#> 18 39 9 11 13 13 34 17 82 0 2 10 23 97 63 44 47 30 48 90
#> WQ3 WT1 WT2 WT3
#> 24 5 6 6
#>
#> $t.occ
#> aacu amin apur bbip bcan ccer clam cort ctri dbre dper druf eful estr ffau hobv
#> 3 23 7 12 3 4 3 5 5 2 15 2 1 8 10 10
#> iiso mbor mobs odol ogla pinc ppyg pvic tuni vcos vicr vidi
#> 4 1 3 1 2 7 10 13 8 1 1 12
#>
#> $t.abu
#> aacu amin apur bbip bcan ccer clam cort ctri dbre dper druf eful estr ffau hobv
#> 4 86 8 25 3 5 4 7 40 4 56 3 2 14 36 37
#> iiso mbor mobs odol ogla pinc ppyg pvic tuni vcos vicr vidi
#> 17 5 5 13 4 16 245 18 17 2 1 54
#>
#> $ntot
#> [1] 731
#>
#> $mfill
#> [1] 0.2619048
#>
#> $nsamp
#> [1] 24
#>
#> $ntaxa
#> [1] 28
#>
#> $nsegm
#> [1] 2
#>
#> $segment
#> [1] "fresh" "broken"
#>
#> $call
#> mefa(xtab = stcs(dol.count), samp = dol.samp, taxa = dol.taxa)
#>
#> $nested
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $drop.zero
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $xtab.fixed
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> attr(,"nlist")
#> [1] 10
## Testing mefa objects
is(x4, "mefa")
#> [1] TRUE
## Removing empty samples
as.mefa(x4, drop.zero = TRUE)
#>
#> An object of class 'mefa' containing
#>
#> $ xtab: 731 individuals of 28 taxa in 23 samples,
#> $ segm: 2 (non-nested) segments:
#> broken, fresh,
#> $ samp: table for samples provided (2 variables),
#> $ taxa: table for taxa provided (4 variables).
#>
## Dimensions
dim(x4)
#> [1] 24 28 2
## Dimnames
dimnames(x4)
#> $samp
#> [1] "DQ1" "DQ2" "DQ3" "DT1" "DT2" "DT3" "LQ1" "LQ2" "LQ3" "LT1" "LT2" "LT3"
#> [13] "RQ1" "RQ2" "RQ3" "RT1" "RT2" "RT3" "WQ1" "WQ2" "WQ3" "WT1" "WT2" "WT3"
#>
#> $taxa
#> [1] "aacu" "amin" "apur" "bbip" "bcan" "ccer" "clam" "cort" "ctri" "dbre"
#> [11] "dper" "druf" "eful" "estr" "ffau" "hobv" "iiso" "mbor" "mobs" "odol"
#> [21] "ogla" "pinc" "ppyg" "pvic" "tuni" "vcos" "vicr" "vidi"
#>
#> $segm
#> [1] "fresh" "broken"
#>
## Simple examples how to use mefa objects in analyis
## GLM on sample abundances
mod <- glm(summary(x4)$s.abu ~ .^2,
data = x4$samp, family = quasipoisson)
summary(mod)
#>
#> Call:
#> glm(formula = summary(x4)$s.abu ~ .^2, family = quasipoisson,
#> data = x4$samp)
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 2.5123 0.5476 4.588 0.000303 ***
#> microhablitter -1.1260 1.1066 -1.018 0.324035
#> microhablive.wood -0.7777 0.9760 -0.797 0.437229
#> microhabrock 1.1849 0.6258 1.893 0.076532 .
#> methodquadrat 0.5787 0.6841 0.846 0.410055
#> microhablitter:methodquadrat 1.8267 1.2150 1.504 0.152187
#> microhablive.wood:methodquadrat 1.6756 1.0905 1.537 0.143944
#> microhabrock:methodquadrat -0.1650 0.7876 -0.210 0.836672
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> (Dispersion parameter for quasipoisson family taken to be 11.09643)
#>
#> Null deviance: 574.42 on 23 degrees of freedom
#> Residual deviance: 182.64 on 16 degrees of freedom
#> AIC: NA
#>
#> Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
#>
## See the demo and vignette for more examples
# demo(mefa)
# vignette("mefa")
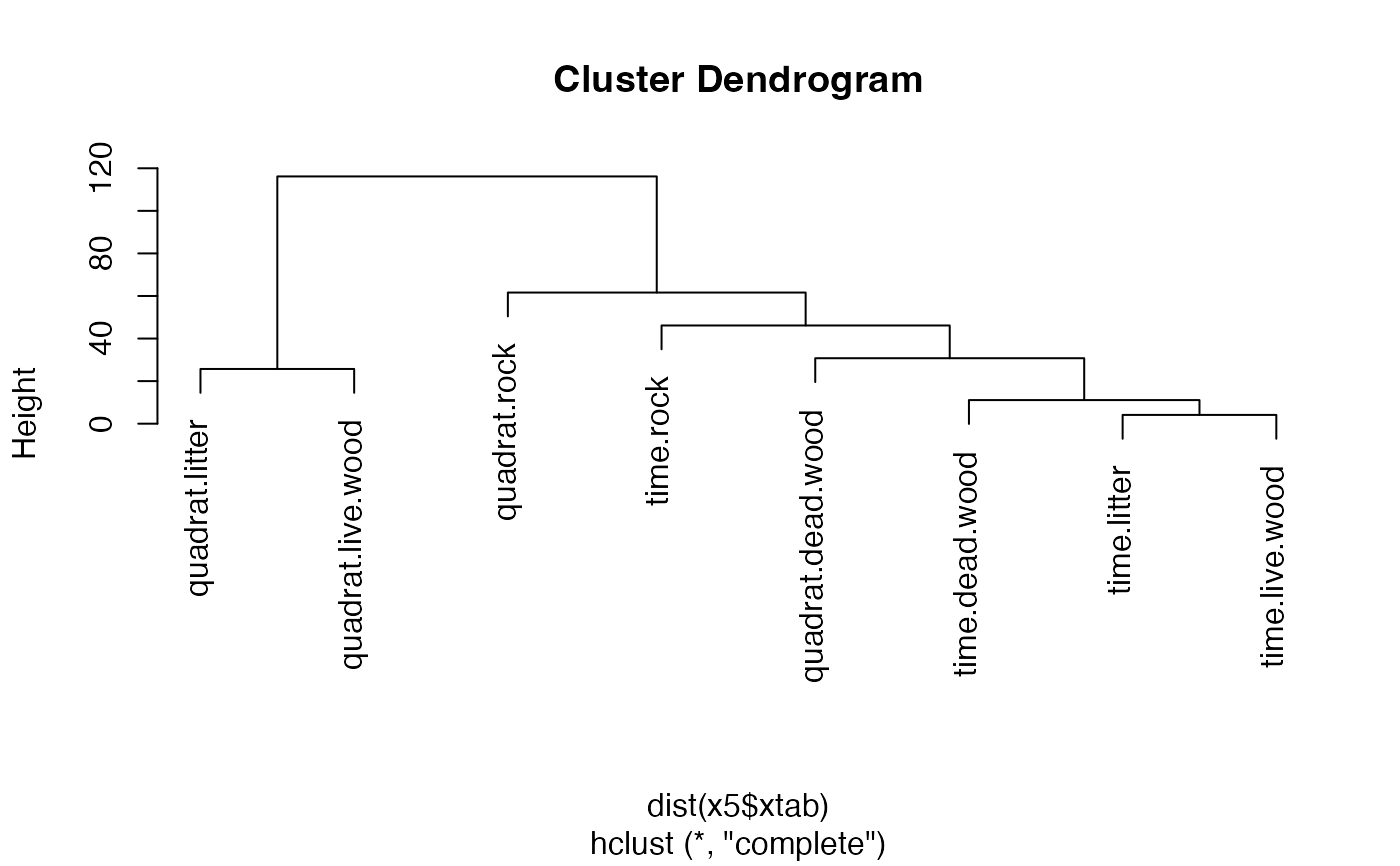
## Cluster analysis of community matrix
x5 <- aggregate(x4, c("method", "microhab"))
h <- hclust(dist(x5$xtab))
plot(h)